What is a Grid Roller and How is it Used: The Ultimate Guide
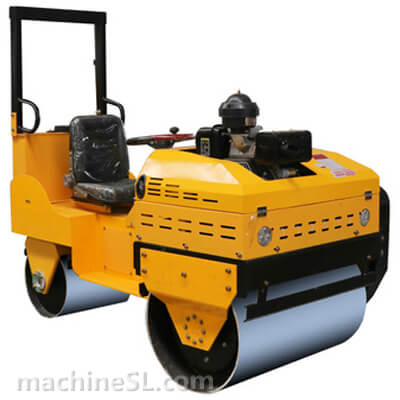
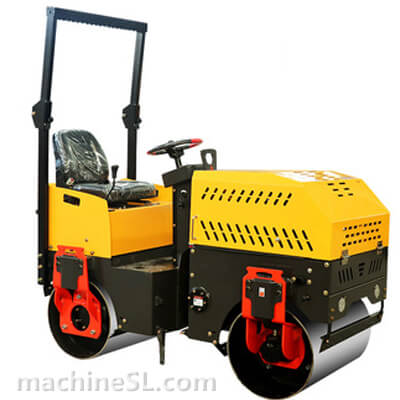
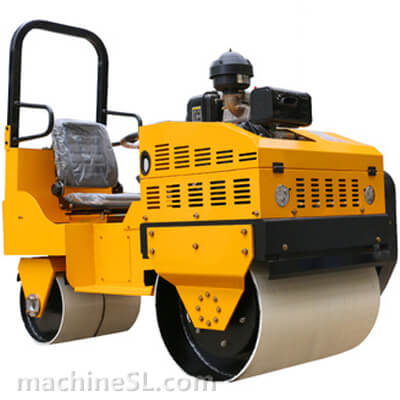
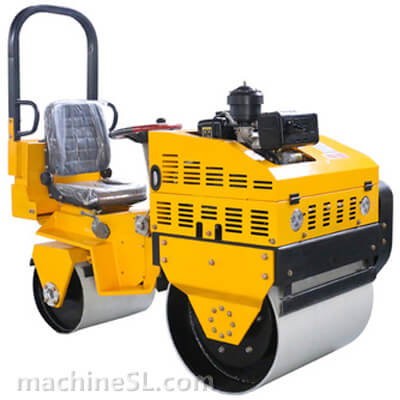
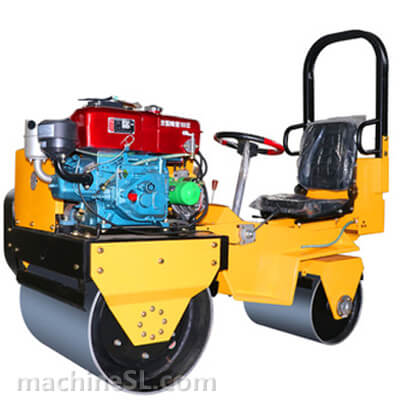
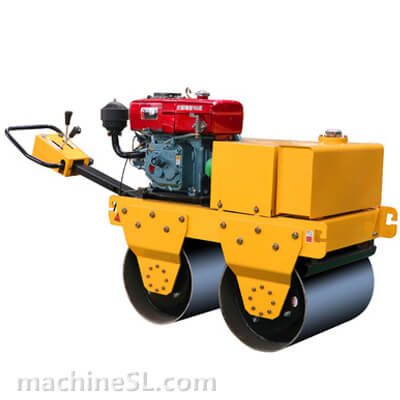
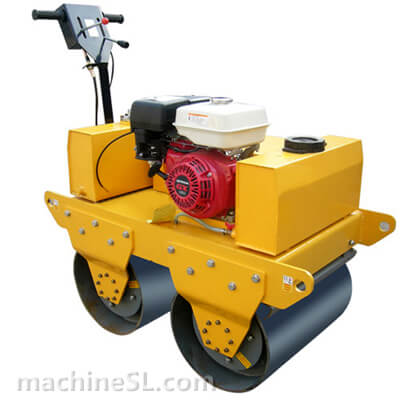
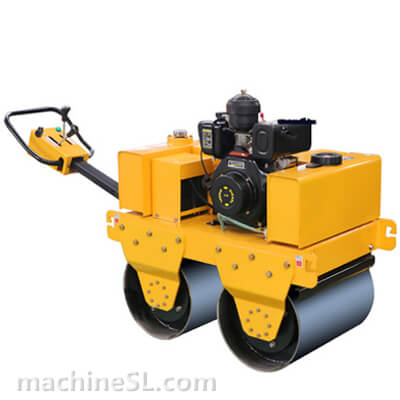
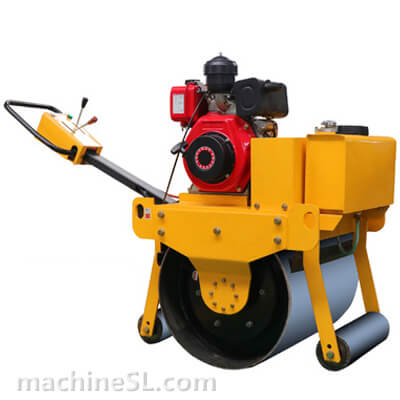
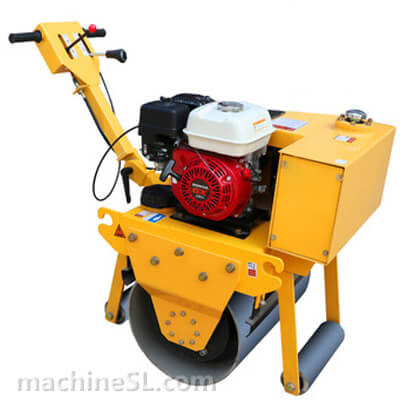
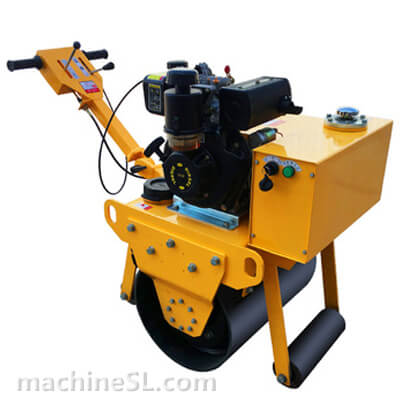
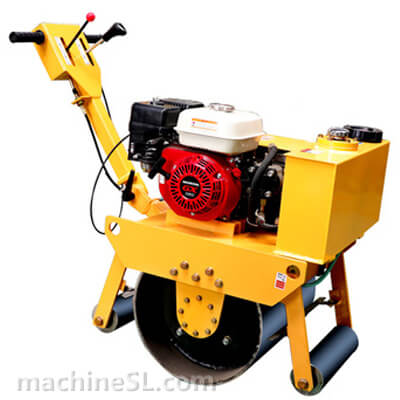
Rollers are designed to meet specific compaction requirements. A grid roller is a static or vibratory roller with rectangular grids on the drum. The grids are made of tough steel to withstand the weight of the drum are it rolls over soil and other materials under compaction. Like other roller types, a grid roller is powered by a diesel engine and has the drum attached to the front or rear. It has a cabin that houses the operator, controls, and other roll over protection components such as seat belts.
Its purpose and functionality
Grid rollers are designed for compaction in projects that require a higher density than normal rollers would achieve. The grids reduce contact area with the material under compaction resulting in increased pressure for maximum compaction. The roller is driven over material severally until the desired density is achieved. These rollers are suitable for compaction in cohesive soils.
Contents
Function of a Grid Roller
A. Explanation of Compaction in Construction
Compaction is the close packaging of material particles to attain a higher density through application of an external force. Compaction force is applied vertically with the aid of weighted objects, in this case, a roller drum. By applying vertical force on construction material, air pockets are eliminated; the space is then occupied by material particles resulting in a higher density.
B. Importance of Compaction
Compaction eliminates air pockets from soil and other surface construction material. When surfaces are exposed to high temperatures, the air within the material expands. This causes a forced displacement of particles resulting in cracks and rutting for asphalt surfaces. The close packaging of material particles limits their movement as they are bonded by friction on their surfaces. The limited movement prevents settling of the material when the surface is subjected to traffic loads in roads or structural loads in buildings.
C. Role of Grid Rollers in The Compaction Process
Compaction is done at different levels. Grid rollers are used in scenarios where a high degree of compaction is needed. The steel grids on the roller penetrate the material under compaction to greater depths than other roller types. The deep compaction ensures the material is densely packed through all its layers.
Key Features and Components
A. Grid Rollers Structure
A grid roller consists of a sturdy frame that supports a cylindrical drum. The drum is the primary compaction component and has a grid pattern. It is mounted on bearings, allowing it to rotate freely. The roller is powered by an engine and equipped with a hydraulic system for controlling movement, compaction force, and optional vibration. The operator’s compartment houses controls and instrumentation, while a ROPS provides operator safety. Some grid rollers have a water tank for moistening materials, and certain models may feature articulation or steering mechanisms for maneuverability.
B. Essential Components and Their Functions
The essential components of a grid roller and their functions are as follows:
- Frame- Provides structural support and stability to the roller.
- Drum- The main compaction component, which has a grid pattern. It applies pressure to the material being compacted, ensuring proper compaction. Compaction could be solely dependent on the weight of the drum or on the drum vibrations as well depending on the roller design.
- Bearings- Allow the drum to rotate smoothly and efficiently.
- Hydraulic System- Powers various functions of the roller, such as movement, compaction force adjustment, and optional vibration for enhanced compaction performance.
- Engine- Provides power to drive the roller and operate its hydraulic system. Being heavy equipment, most grid roller engines are diesel powered.
- Operator’s Cabin- Contains controls, instrumentation, and a comfortable seating area for the operator to control and monitor the roller’s operations.
- ROPS (Roll-Over Protective Structure)- Ensures the safety of the operator by providing a protective structure in case of rollover or accidents.
- Water Tank or Water Distribution System- Used to moisten the material being compacted, reducing friction and improving compaction efficiency. Water tanks and distribution systems are found in some grid roller designs while others use external water sources for compaction.
- Articulation or Steering Mechanism- Enables maneuverability on uneven terrain and controlled movement of the roller. Some grid rollers have a hydraulic steering system for easy control and maneuverability.
C. Different Types and Sizes of Grid Rollers
Grid rollers come in various types and sizes to suit different compaction needs. They can be classified based on drum design and operation such as static grid rollers and vibratory grid rollers. Sizes vary from small compactors used for light compaction to large heavy-duty rollers for extensive projects. Grid rollers are available in different weight capacities, typically ranging from a few tons to over 20 tons. The specific type and size of grid roller chosen depend on factors like the type of material, project size, and desired compaction results.
Applications of Grid Rollers
A. Road Construction and Maintenance
Roads are subjected to heavy traffic loads and extreme weather conditions. For durability, deep compaction of the base and subbase layers is necessary. Grid rollers can attain in-depth compaction of materials ensuring air pockets are eliminated and the material particles are densely packed together. Elimination of air pockets prevents surface cracking and rutting when the road is exposed to hot weather. Dense material particles packing prevents settling of the base and sub base when the road is subjected to traffic loads.
B. Landfill Construction and Compaction
Grid rollers play a crucial role in landfill construction and compaction. They are used to compact and stabilize the waste material in landfills, reducing voids and increasing density. By applying pressure, grid rollers ensure proper compaction, which minimizes settlement and improves the structural integrity of the landfill. This compaction helps prevent the release of harmful gases, enhances waste containment, and promotes overall landfill stability and longevity.
C. Airport Runway and Taxiway Construction
Runway and taxiway construction process is similar to road construction. To prevent cracking of the asphalt surface, the base and subbase layers need to be well compacted. This helps sustain impact and traction loads generated by landing planes on the runway.
D. Sports Field and Racetrack Construction
Grid rollers are employed in the construction of sports fields and racing tracks to achieve proper compaction of the base and sub-base materials. By compacting the soil or aggregate layers, grid rollers create a stable and uniform surface that enhances the performance, safety, and longevity of sports fields and racing tracks.
E. Other Potential Applications
In addition to road construction, landfill compaction, and sports field construction, grid rollers have potential applications in various areas. These include the construction of airfields, dams, embankments, and railway tracks. They can also be used for compaction in industrial sites, residential developments, and any project requiring soil, asphalt, or material compaction for improved stability and load-bearing capacity.
Advantages of Using a Grid Roller
A. Enhanced Compaction Efficiency and Effectiveness
Grid rollers offer enhanced compaction effectiveness and efficiency due to their specialized design. The grid pattern creates a kneading effect, breaking up air voids and achieving greater density. This results in improved compaction, reduced settling, and increased stability of the compacted material.
B. Increased Productivity and Time Saving
Engine driven grid rollers complete more work within a short period compared to alternative compaction methods. This helps minimize labor demand and reduce construction time.
C. Improved Stability and Soil Bearing Capacity
Deep compaction by grid rollers packs soil particles tightly together limiting their movement. As a result, the soil can sustain higher loads without settling. This allows heavy construction to be carried out of the compacted soil.
D. Reduction of Long-Term Maintenance Costs
Compaction in road construction is essential. When done by grid rollers, the subbase and base layers of the road can sustain heavy traffic loads without settling or cracking when exposed to intense heat. Water percolation which reduces road quality is eliminated keeping the road durable and minimizing maintenance costs.
Operating a Grid Roller
A. Preparing The Work Area
Before operating a grid roller, it is essential that the site be prepared for efficient compaction and safety of the roller. All unwanted material and debris should be removed from the site as they can alter compaction results or cause damage to the roller. The site should be cordoned off and only authorized persons allowed to access. This prevents accidents and injury to third parties. Lastly, the site markings and signage should be made visible and elaborate to guide the operator.
B. Safety Precautions and Guidelines
- Operators should receive proper training on equipment operation and safety procedures.
- Wear appropriate personal protective equipment, including a helmet, safety vest, and steel-toed boots.
- Conduct a pre-operation inspection to ensure the roller is in good working condition.
- Observe proper traffic control measures on the work site.
- Maintain a safe distance from other workers and obstacles.
- Adhere to weight and compaction limits to avoid overloading and instability.
- Monitor and adjust compaction force as needed.
- Regularly inspect and maintain the roller for optimal performance and safety.
C. Step-by-step Instructions for Operating a Grid Roller
1. Pre-Operation Inspection
- Check for any visible damage or leaks.
- Ensure all safety features, such as ROPS, seatbelt, and lights, are functional.
- Check fluid levels, including fuel, hydraulic oil, and water (if applicable).
- Inspect tires or tracks for proper inflation and condition.
- Verify that all controls and instruments are working correctly.
2. Safety Precautions
- Wear appropriate personal protective equipment.
- Familiarize yourself with emergency shut-off procedures.
- Ensure the work area is clear of obstacles and personnel.
3. Start-Up
- Get into the operator’s compartment and fasten the seatbelt.
- Start the engine following the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Engage the parking brake.
4. Operating Controls
- Familiarize yourself with the control layout, including throttle, steering, and compaction force adjustment (if applicable).
- Understand the operation of any additional features, such as vibration or water spray.
Movement and Steering:
- Release the parking brake.
- Use the steering mechanism or articulation (if applicable) to guide the roller.
- Maintain a safe speed and avoid sudden changes in direction.
5. Compaction
- Lower the drum onto the material to be compacted.
- Drive the roller forward in a straight line, overlapping each pass.
- Monitor the compaction effectiveness by observing the material response and compaction meter (if available).
- Adjust the compaction force as needed based on the material and desired compaction results.
6. Watering (If Applicable)
- Activate the water spray system to moisten the material for improved compaction.
- Adjust the water flow rate as necessary.
7. Shutdown
- Park the roller on a level surface away from traffic or hazards.
- Engage the parking brake.
- Turn off the engine following the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Conduct a post-operation inspection and report any issues or concerns.
This is a general guide, and it is crucial to refer to the specific equipment’s manual and receive proper training before operating a grid roller.
D. Maintenance and Troubleshooting Tips
- Regularly inspect and clean the roller, removing debris and dirt buildup.
- Lubricate moving parts according to the manufacturer’s recommendations.
- Check and replace worn or damaged parts, such as bearings or drum segments.
- Monitor fluid levels and perform regular fluid changes.
- Keep the hydraulic system clean and check for leaks.
- Address any abnormal noises or vibrations promptly.
- Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for scheduled maintenance and consult a professional for complex issues.
Conclusions
Grid rollers are vital construction vehicles used for achieving stable surfaces in various applications. They play a crucial role in road construction, landfill compaction, sports field creation, and more. By effectively compacting soil, asphalt, and other materials, grid rollers enhance load-bearing capacity, durability, and overall stability.
They create uniform and dense surfaces, minimizing settling and improving longevity. Grid rollers ensure optimal compaction through their specialized design, such as grid patterns, which break up air voids and increase material density. Their significance in construction cannot be overstated, as they contribute to the safety, performance, and longevity of infrastructure projects.




















Leave A Comment