Soil Compaction in Construction: A Complete Guide
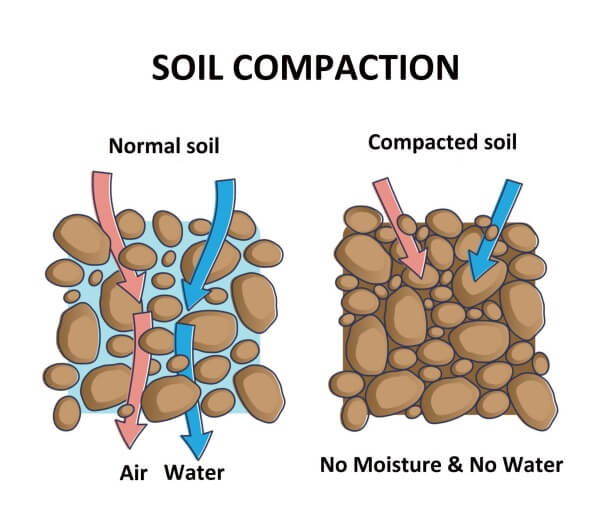
Soil compaction is one of the basic processes for increasing soil density. Through this process, mechanical pressure eliminates air voids. Moreover, this procedure increases soil stability, durability, as well as bearing capacity. That’s why it is a critical step in infrastructure development. An appropriate compaction level controls structural failure and reduces maintenance costs too. It ensures the safety and long life of buildings, roads, and other construction works.
In this blog, we will explore the significance of soil compaction. Along with the different methods, we will discuss the suitable equipment. Moreover, the influencing factors and the industrial practices are below here.
Contents
What is Soil Compaction

Soil compaction is a mechanical process for increasing the soil density. Usually, it expels the air from the soil particles to enhance load-bearing capacity. Usually, this is a mechanical process. It carries out by rollers and compactors. Compaction is necessary for foundation that withstands structural load. In the case of roads, they can bear loads of heavy traffic only if the soil is compact.
Various construction projects need different degrees of compaction. Due to environmental conditions and soil type, each project has its compaction need. Factors such as moisture content, soil gradation, and effort determine its effectiveness.
Why is Soil Compaction Important in Construction
The question “why we need soil compaction in construction” is important to understand. Here are some common points to grasp the idea of compaction in construction projects.
- Structural Stability – Compacted soil prevents settlement and ensures the structure’s reliability. A well-compacted base gives a strong foundation. This helps ensure long-term stability.
- Load Bearing capacity of soil – A compact soil surface has higher density. It can support the greatest loads without settling or shifting. Thus, it is a must to compact soil for preventing structural failures.
- Erosion Control – Compaction helps in controlling erosion by reducing air gaps in soil. The absence of air voids will reduce water infiltration and runoff. It also prevents soil displacement, landslides, and damage to retaining walls and embankments.
- Pavement and Road Durability – Compaction creates strong base for pavement and reduces cracks. It also extends the life of highways and decreases the long-term repair costs.
- Soil Shrinkage and Expansion – The higher the clay content, the higher the shrinkage. It will also expand with a change in moisture level. Adequate compaction eliminates the chances of volume changes and prevents foundation cracks. It also addresses the uneven surfaces and damages to underground utilities.
- Drainage Improvement – A good compacted soil can provide proper drainage. It ensures that the water does not pool beneath the structures and roads. Hence, it prevents frost heave and soil weakening.
Understanding Soil Types and Their Impact on Compaction
Degree of compaction depends on the type of structure and strata. There are different types of soils possessing variable effects on compaction. Moreover, conducting a soil test to understand soil type is mandatory before compaction. It can ensure the best results and prevent project failures. We have discussed in detail as below:
- Cohesive Soils– This type of soil contains fine particles; silt and clay lie in this category. As clay retains moisture, it requires high compaction efforts.
- Non–cohesive soils – non-cohesive soils are also called granular soils. Compaction is easy due to their granular nature. Yet, they may need stabilizing agents and additives.
- Loam Soils – These soils are a mixture of sand, silt, and clay. These soils offer balanced compaction properties and make them ideal for construction.
Factors Affecting Soil Compaction
There are many factors that affect the compaction. Sometimes it enhances or may decrease the efficiency. Let’s have a wider look here!
Moisture Content – Moisture content plays an important role in various properties of soils. The same is the case for compaction. The accurate moisture level or best moisture content enhances compaction efficiency. Yet, higher or lower moisture content can impact the compaction process.
Type of Soil – Different type of soils behave different towards compaction. It requires specific techniques to achieve the good level of compaction.
Compaction Effort – Efficiency is also dependent upon the effort put in compaction. The higher mechanical force applied will lead to higher level of compaction.
Layer Thickness – Adequate thickness of layer give us uniform compaction. It also prevent weak layers.
Soil Compaction Methods & Best Practices
Globally there are many methods of carrying out compaction of soils. But, some of the best practices are present in this article.
- Static Force Compaction – This method utilizes the heavy machinery i.e., drum roller. This method is applicable for fine-grained soils.
- Vibratory Compaction– Vibratory compaction works by generating vibrations in the soil. It rearranges the soil particle with less air void. So, it is suitable method for granular soils.
- Impact Compaction – For impact compaction, soil densification requires a high -impact energy.
- Kneading Compaction – This compaction uses repeated kneading action to compact the clay-rich soils.
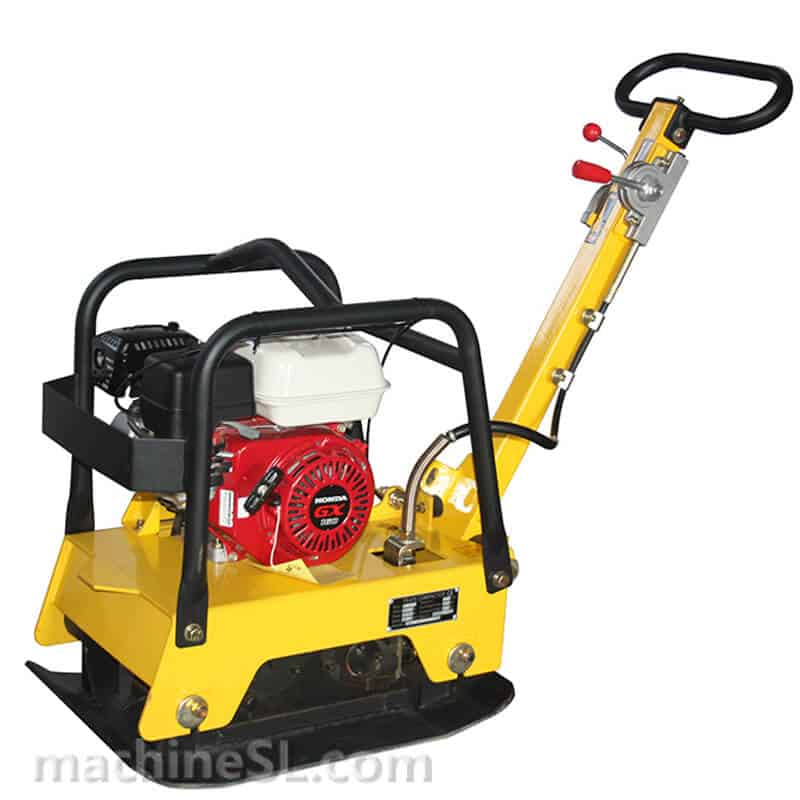
Equipment Used for Soil Compaction
- Heavy Rollers – Heavy rollers are suitable for large-scale compaction. It includes smooth, pad foot, and pneumatic tire rollers.
- Smooth Drum Rollers – It is for compacting granular and well-graded soils. Drum roller is effective in large-scale projects such as road construction.
- Pad foot Rollers – This roller is ideal for compacting cohesive soils like clay. It works by using tamping feet that penetrate the soil, improving density.
- Pneumatic Tire Rollers – Pneumatic tire roller features many rubber tires. These tires provide uniform pressure. The pressure make them suitable for compacting asphalt layers and granular soils.
- Grid Rollers – it is a heavy cylindrical steel rollers with a grid pattern. Grid rollers help break down oversized particles and compact coarse-grained soils.
- Sheepsfoot Rollers – Sheepsfoot roller is for compacting fine-grained soils. The protruding lugs help knead and compact clay-heavy soils.
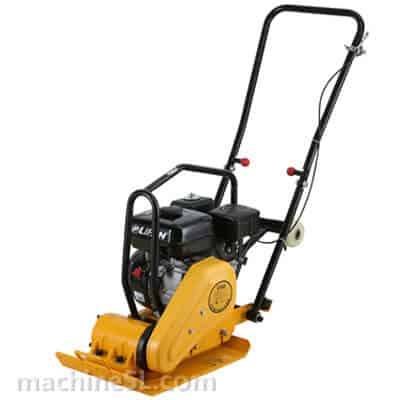
- Vibratory Plate Compactors – It is ideal for compacting granular soils in confined areas. These machines use a vibrating base plate to create compaction through repeated impacts.
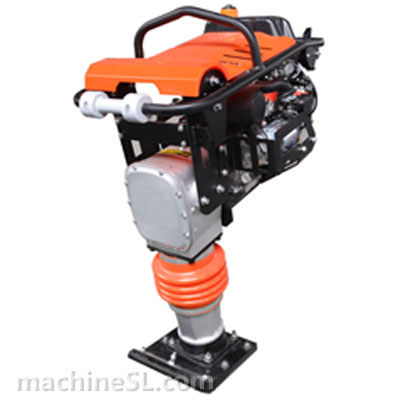
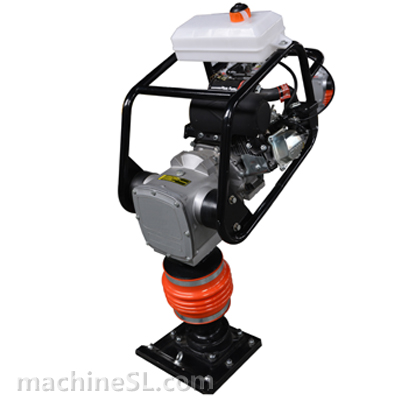
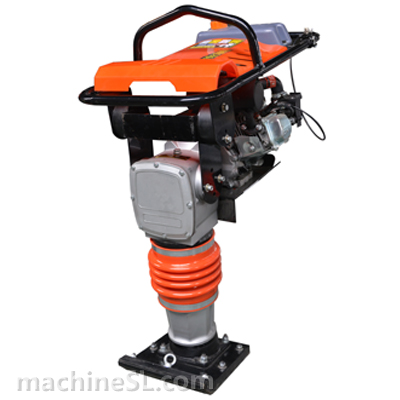
- Rammers & Tampers – Both tampers and rammers are for compacting small spaces. For example, trenches, foundations, and small spaces. They generate high-impact force and are most effective for cohesive and mixed soils.
- Jumping Jack Compactors – As a variation of rammers, it deliver a high-frequency impact. These are particularly useful for compacting soil in narrow or difficult-to-reach areas.
- Towed Compactors – This compactors is a non-motorized compactor connect to a vehicle. They are often used in large-scale compaction projects like highway construction
Achieving Proper Compaction: Industry Standards
Construction projects need maximum dry density of soil which is achievable by compaction. Moreover, monitoring of soil density, moisture levels ensures compliance with standards and specifications. Many laboratory and field tests are available to ensure the best compaction of soil. To check the compaction level, following standards are available.
- Laboratory Testing Methods
- SPD & MPD – It stands as standard proctor density (SPD) and modified proctor density (MPD. As per industrial standard a 95% of SPD or MPD should be achiever to ensure stable soil. This test determines optimal dry density of soil and its optimal moisture content.
- Field Testing Methods
For field testing, following tests are common in industrial practices.
- Sand Cone Test – It measures the in-situ soil density. For this test, we replace soil with dry sand to calculate compaction levels.
- Nuclear Density Test – This test uses a nuclear gauge to fix soil density and moisture levels. Use of nuclear gauge ensure rapidness and accuracy of compaction.
- Plate Load Test – Plate load test evaluates the bearing capacity of compacted soil. Application of a static load measures the soil deformation.
- Penetrometer Test – It determines the soil strength and quality of compaction. It uses a probe that measures the soil resistance.
Addressing Challenges in Soil Compaction
Due to different circumstances, it is hard to achieve the best soil compaction. These challenges are inclusive of:
Too Wet or Too Dry Soil
Moisture content is a crucial factor for compaction. Adjustments (adding water or aerating soil) are compulsory for the required compaction results.
Difficult Terrain
For terrain i.e., rocky ground, or unstable soil, it is hard to achieve best density by ordinary methods. Hence, specialized techniques and equipment are essential for compact slopes.
Environmental Considerations
Compaction may get difficult or need higher efforts due to environmental conditions. It can be high natural moisture, extreme hot weather or any other. So, green alternatives, i.e., stabilizers are good for minimizing the environmental impact.
Pros and Cons of Soil Compaction in Construction
Let’s discuss the merits and demerits of compaction in construction.
Merits
- Proper compaction increases the soil stability. It makes the soil suitable for supporting heavy structures.
- Compaction minimizes the ground subsidence, preventing damage to foundations and pavements. It also reduces the chances of soil settlement.
- Compacted soil helps pavements last longer with fewer repairs. Hence, it enhances the road durability
- Soil compaction helps to prevent waterlogging and soil erosion, reducing long-term maintenance needs.
- By compaction of soil, it ensures that the ground can withstand high-pressure loads. It can capable of bearing loads from vehicles, machinery, and buildings.
Demerits
Compaction not only facilitates the construction but also poses negative impact such as:
- Over compaction may lead to drainage problems by making soil impermeable and. It can cause water retention and poor drainage.
- For landscaping, soil compaction can restrict the root and plant growth.
- For tough conditions, and strict circumstances, achieving proper compaction may need specialized equipment. Likewise, the skilled labor, and increased operational costs are necessary.
- In compaction, if it is not proper, it can lead to weak spots that compromise structural integrity.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Soil Compaction
As construction is a human activity and soil compaction can be mistaken sometimes. Following are some of the mistakes which are common during construction.
- Wrong Equipment Use
- Appropriate equipment according to the soil strata/ terrain and environmental condition is important. So, incorrect machinery or method can lead to ineffective compaction and structure failure.
- Skipping Moisture Control
Ignoring the moisture of soil can be a hindrance in achieving the optimal density. Moreover, over-dry or wet soil can encumber compaction efficiency and compromise soil strength.
- Thickness of Layers
Layer thickness matters in achieving the best compaction grade. Thick soil layers make it difficult to achieve uniform density. Thus, compacting in 6–12 inch lifts ensures effectiveness.
- Ignoring Soil Tests
Quality check is mandatory to ensure the safe and recommended compaction level. Hence, failing to conduct soil tests prior compaction can result in poor performance.
- Not Considering Weather Conditions
Rain, extreme heat, or cold can affect compaction results. That’s why adjusting methods based on weather ensures consistency.
FAQs
What methods can confirm suitable soil compaction?
The field tests such as Sand Cone Test and Plate Load Test provide compaction degree.
Soil stabilization represents significant operations compared to compaction. These techniques have different objectives and approaches.
Soil compaction reaches optimum density by reducing air void . Whereas soil stabilization is adding cement or lime materials to enhance properties.
At what depth should I perform soil compaction procedures before building operations start?
Soil compaction, standards allow a 6-12 inches thick layer. Yet, the final depth depends on these factors.
What series of consequences take place when soil receives inadequate compaction?
Improper compaction produces several negative effects including settlement failures. Moreover, erosive conditions alongside diminished load capabilities is also possible.
Can over-compaction be a problem?
Over-compacting soil is problematic when it reduces drainage performance. It increases stiffness levels and produces structural cracks.




































Leave A Comment