Road Roller:A Beginner’s Guide to Construction’s Equipment
Road and pavement construction are among the most demanding projects in the construction industry. Besides having experienced and skilled personnel, you need a wide range of equipment to attain the required standards. Standards vary depending on the type of road and expected traffic load; this determines the choice of equipment used.
Road rollers are common pieces of equipment found in road construction sites. The primary function of road rollers is compacting soil and other construction materials to required densities. There are two main types of road rollers; vibratory rollers and static road rollers. The operation mechanism of the rollers varies; thus, their application is dependent on the stage of construction.
Contents
Purpose and Function of Road Rollers
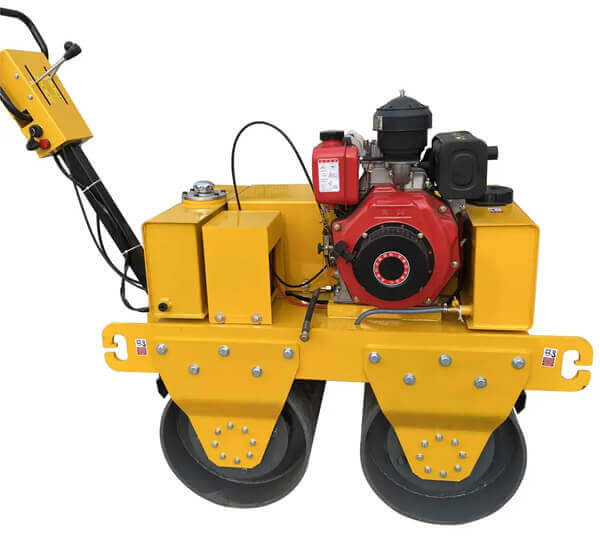
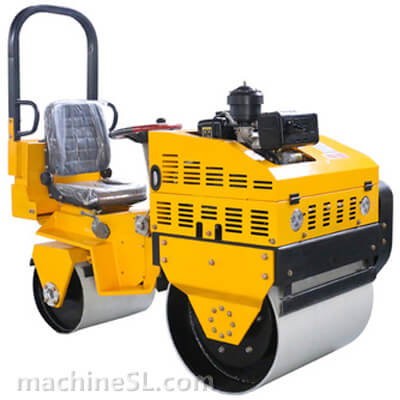
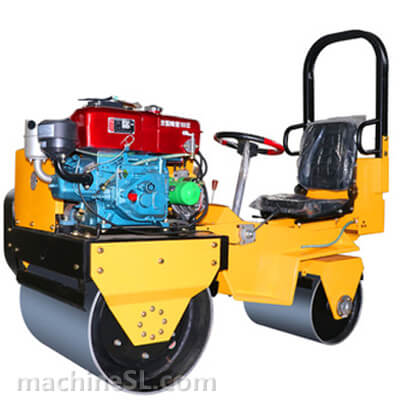
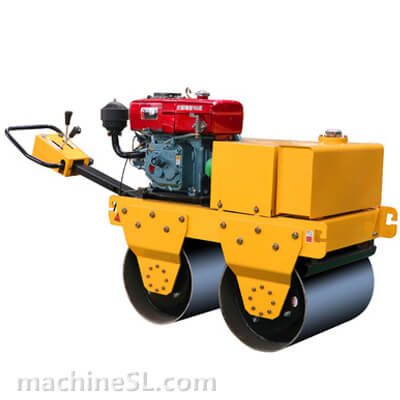
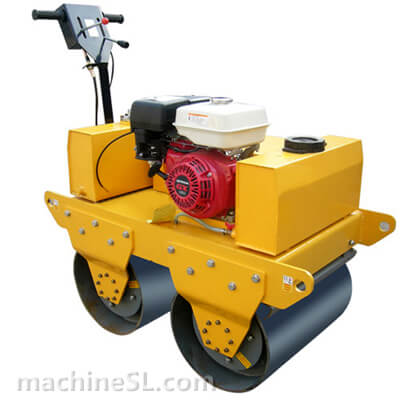
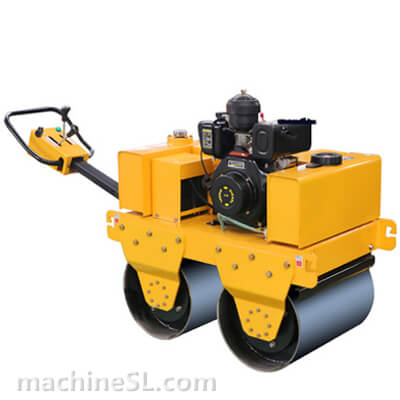
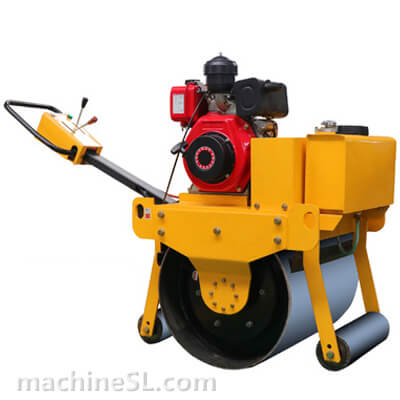
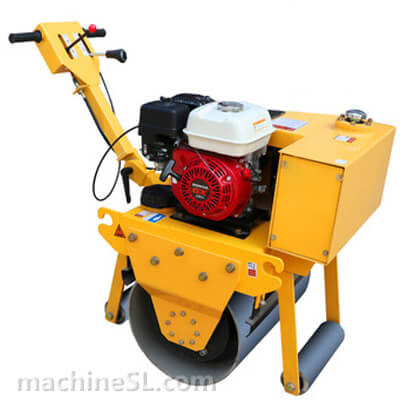
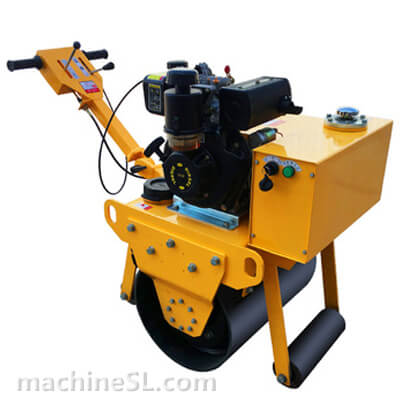
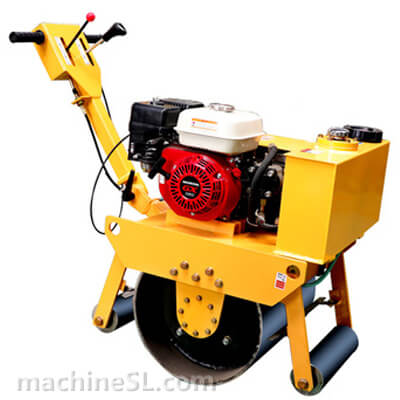
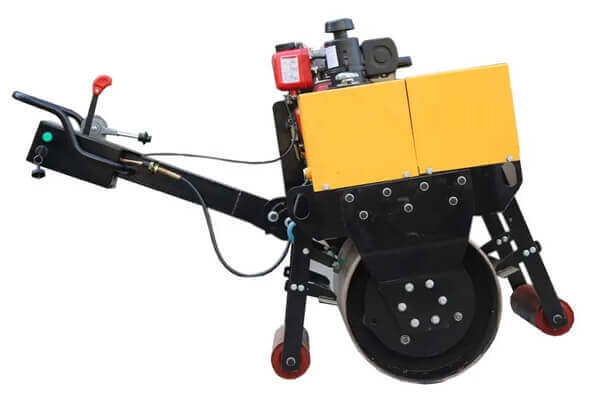
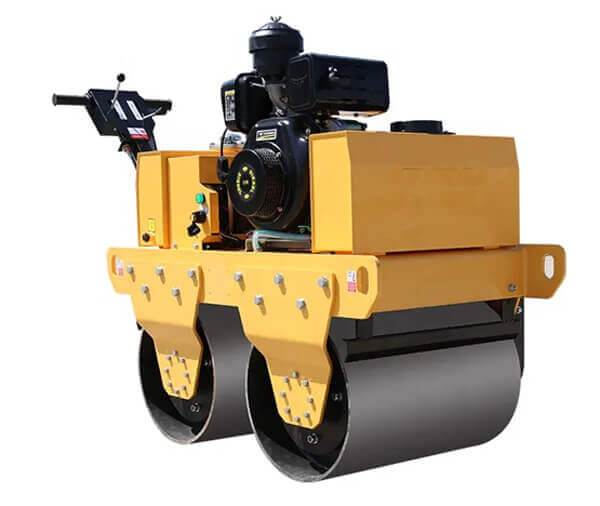
A road roller is a compaction equipment made of a roller/ drum and an engine. It utilizes the weight of the drum and engine power to exert compaction force through vibrations. Depending on the need, road rollers could have smooth, padded, or spike-installed drums. The drums are usually attached to the front or at the back of the roller.
The primary role of road rollers is compacting materials to required densities in the construction of road bases. Road base material need to be properly compacted to avoid settling; which might lead to surface cracking, after road construction. In asphalt paving, road rollers are used to compact the asphalt concrete to required standards.
Additionally, they smooth and level surfaces, creating an even and uniform base for further construction. Road rollers prepare the ground for asphalt or concrete application, ensuring a solid foundation that enhances the durability and longevity of roads, pavements, and other infrastructure projects.
Function and Components of Road Rollers
Road roller’s main function in construction is compaction. There are various needs for compaction; these dictate the size and type of road rollers you choose. In road construction, road rollers are used to compact the road base to the required densities. In asphalt paving, road rollers are used to compact the asphalt concrete into place.
Structural construction can also involve the use of road rollers. For large-scale high-rise buildings, a road roller can be used to compact the ground for a stable base to support the foundation. In environmental management and construction waste disposal, rad rollers are used to compact waste to required densities. Waste or dirt compaction allows for the storage of large volumes and keeps waste for a longer period without affecting the environment.
The functioning of a road roller involves the working of various components. These are discussed in detail below;
- The engine- This is the main component of the road roller. Engines vary in capacity depending on the size of the road roller. Smaller engines are usually petrol powered. However, the most common engines are diesel-powered due to their capacity to handle heavy drums for long hours.
- Drum- This is the compaction interface. The drum comes in contact with the material under compaction. The weight of the drum combined with the vibration generated in the engine forces particles to settle into a denser state.
- Steering mechanism- Compaction requires the road roller to move in different directions. The maneuvers are made possible by a steering mechanism. The steering controls both the rear wheels and the drum in the operator’s desired direction.
- Braking system- Essential for controlling movement on site, the braking system is responsible for slowing down the roller and/or keeping it at a full stop. There are various types of braking systems; traditional ones are not used in rollers as they are ineffective.
Types of Road Rollers
The two main types of road rollers are the vibratory road rollers and static road rollers. These are discussed in detail below.
Vibratory road rollers
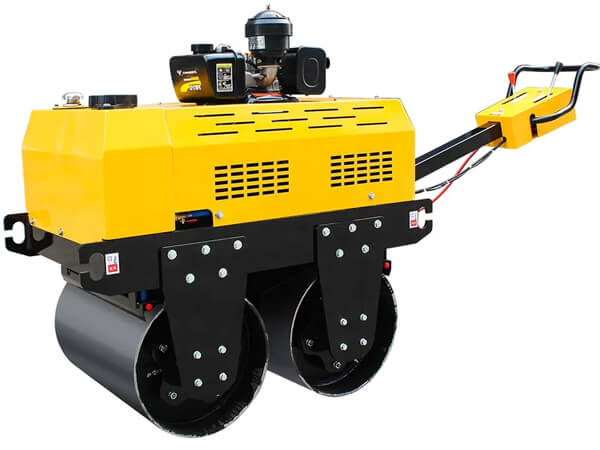
Vibratory road rollers consist of one or two eccentric shafts that rotate rapidly, causing vibrations. These vibrations help to enhance the compaction process by breaking down the air voids more effectively. The advantages of using vibratory rollers include increased compaction efficiency, improved uniformity, and reduced risk of material segregation. They are particularly beneficial for cohesive soils and granular materials.
The initial cost of acquiring vibratory rollers is very high; this discourages their use in private small-scale projects. The heavy engine vibrations result in increased fuel consumption making them uneconomical for small projects. If not properly used, vibratory rollers can easily damage surfaces and cause cracks on nearby structures. Careful consideration of soil type and proper training are necessary to maximize the benefits of vibratory road rollers.
Static road rollers
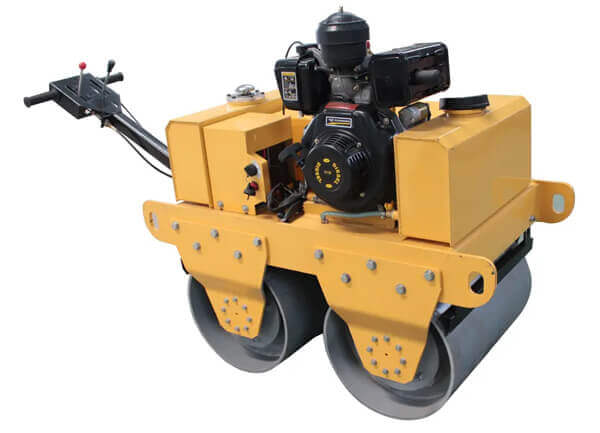
Unlike vibratory rollers, static rollers rely solely on their weight and gravitational force to compact the material underneath. They are commonly used in projects where vibration may cause damage or is unnecessary, such as compacting cohesive soils, clay, and crushed rock.
The advantages of static road rollers include their simplicity, lower maintenance requirements, and lower fuel consumption compared to vibratory rollers. They are also effective in achieving high compaction densities and are generally more cost-effective for certain types of construction projects.
Components and features of road rollers
The functioning of a road roller involves various parts and components working in synchrony. While some elements are directly involved in compaction, others play third party roles such as control and regulation. Critical parts of road rollers are discussed below;
- Engine and power system- The engine drives the wheels or drum through a transmission system, providing the necessary power and torque for the roller to perform its compaction and leveling tasks effectively. Road rollers are heavy and require high power to operate; this is the reason why most of their engines are diesel-powered.
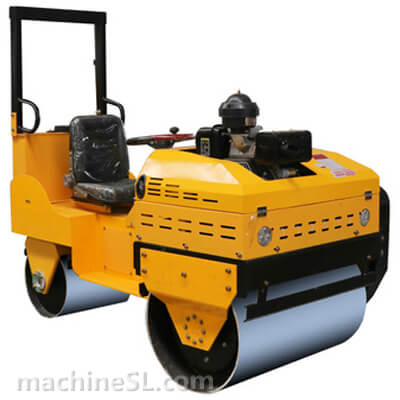
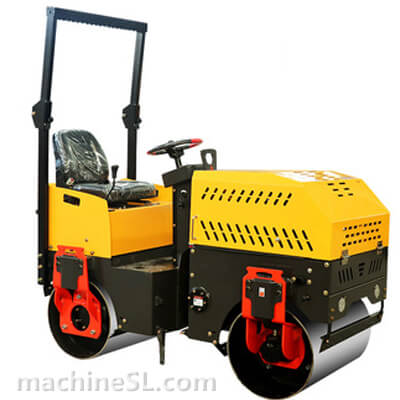
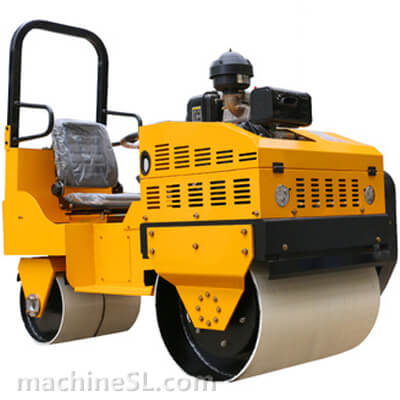
- Roller drum and weight- The roller drum is the compaction interface between the roller and material under compaction. Road rollers utilize the weight of the roller to exert a downward compaction force on the material.
- Steering and control mechanisms– Road rollers typically utilize hydraulic steering systems for control. Steering is achieved by applying differential braking, where the operator can control the braking force on the left and right sides independently. This allows for precise maneuverability and turning. The operator also has control over the speed and direction of the roller, usually through a control lever or joystick, enabling them to navigate and operate the machine with ease and accuracy.
- Safety features and operator cabin– Road rollers are equipped with various safety features such as seat belts, ROPS (Roll-Over Protective Structure), and FOPS (Falling Object Protective Structure) to protect the operator in case of accidents. The operator cabin is enclosed and designed for comfort, visibility, and reduced noise levels, ensuring a safer and more productive working environment.
Operating a Road Roller
Operating a road roller requires proper training and qualifications. Operators typically need to complete a specialized training program that covers equipment operation, safety protocols, and maintenance procedures. They should also have a valid driver’s license and may need additional certifications based on local regulations. It is essential to understand compaction principles, soil types, and safety guidelines. Ongoing training and experience are crucial for staying updated with industry standards and ensuring safe and efficient operation of road rollers.
Effective operation of road rollers involves a series of preparations. These preparations ensure the roller operates at maximum efficiency and prevents unnecessary breakdowns. Before starting the roller, the operator needs to check the fuel and fluid levels, inspect the roller for any visible damage, ensure proper tire inflation, test the lights and signals, and inspect the safety features. They should also conduct a pre-start inspection of the engine, hydraulics, and controls, and verify that all necessary tools and equipment are on board.
Operating a road roller requires adherence to various safety precautions and guidelines. Operators should wear personal protective equipment (PPE) such as helmets, high-visibility vests, and safety shoes. They must follow designated speed limits, be aware of their surroundings, and communicate with other workers on-site. When operating, they should maintain a safe distance from other machinery, avoid sudden maneuvers, and always use the machine’s safety features. Proper compaction techniques, including overlapping passes and consistent speed, should be followed to achieve uniform compaction across the surface. Regular equipment maintenance and inspections are also crucial to ensure safe and efficient operation.
Road Roller Maintenance and Care
Regular maintenance and care are essential for the optimal performance and longevity of road rollers. Routine maintenance includes checking and replacing fluids, inspecting belts, filters, and hoses, and lubricating moving parts according to the manufacturer’s guidelines.
Regular inspection and servicing of key elements like the engine, hydraulic system, brakes, and electrical components are necessary to identify and address any issues promptly. Cleaning the machine regularly helps prevent debris buildup and corrosion.
Common troubleshooting may involve addressing issues with vibration, steering, or braking systems. Repairs might include replacing damaged parts, addressing hydraulic leaks, or fixing electrical malfunctions.
It is recommended to follow the manufacturer’s maintenance schedule and consult professional technicians for complex repairs and troubleshooting.
Conclusions
Road rollers are important in all construction projects. Compaction requirements determine the size of a road roller one chooses. The main parts of a road roller are; the engine, the drum, the steering mechanism, and the braking system. The braking systems in road rollers are designed to ensure safe and controlled operation.
Hydraulic, engine braking and transmission-based braking mechanisms work together to provide efficient stopping power, especially considering the operational characteristics of the roller, such as weight, speed, and terrain. Safety mechanisms, operator training, and adherence to protocols further contribute to mitigating risks and promoting a secure working environment.
By prioritizing safety and employing appropriate braking systems, road rollers can effectively contribute to construction and road maintenance projects while minimizing accidents and protecting personnel.


















Leave A Comment