Compacted Backfill [What is it, Why Compaction, How to Compact]

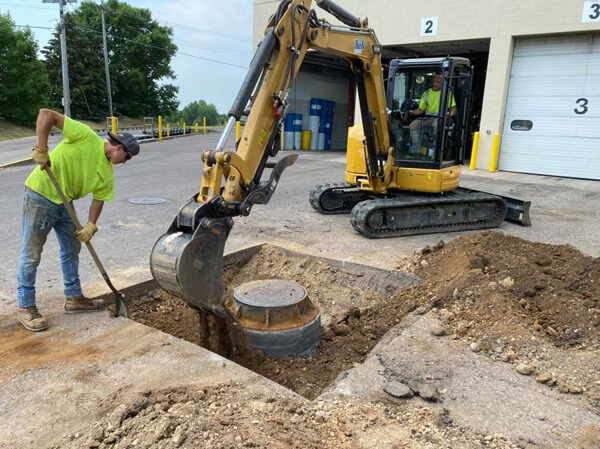
The construction process begins with the excavation, a lot of digging works depending on how big the structure is. The excavated soil are then set aside to be used on the later stage. These are stockpiled and secured that no foreign elements will affect it.
Alongside with the ground works, the excavated material will be tested to determine the actual soil type and properties which will determine if it can be used or placed back or if not, another soil to be used in backfill will be necessary to match with the structural requirement.
The factors that affect your backfill material are:
- Choosing the suitable backfill material
- Compacting the suitable backfill material and
- The time it takes to backfill the area.
Backfilling a foundation is an important process to help protect the structural element. To ensure that the backfill material is right make sure to check if the material sample passed the testing or is approved, required density is achieved and that it is done in layers.
Contents
What is Compacted Fill Material

Compaction, in other word means compressing the soil material. This process is important because it reduces the volume of the total mass of the soil which consists of soil particles, water content & air by application of pressure from different ways like rolling, tamping and vibration.
Compacted fill material are those loose soil that are compacted in layer during the backfilling. The importance of compacting the fill material is to increase the shear strength, decreases its compressibility and decreases its permeability. The fill material can be categorized in two classification of soil which have different ways to effectively compact the material during the backfilling. The two classification are cohesive soil and cohesion less soil.
Cohesive soil are the type of soil that are fine-graded, low-strength and easily deformed soils. These material have significant cohesive strength and can exhibit plasticity. According to OSHA, cohesive soil means clay (fine-grained soil), or soil with a high clay content. Cohesive soil do not crumble, can be excavated with vertical side slopes, and is plastic when moist. Cohesive soil is hard to break up when dry, and exhibits significant cohesion when submerged.
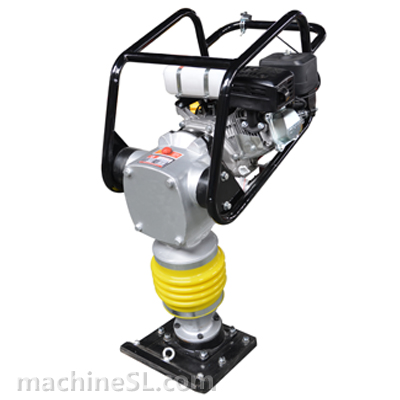
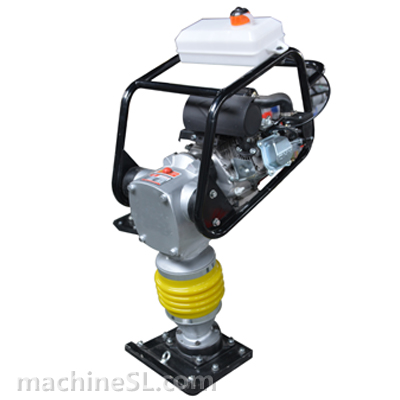
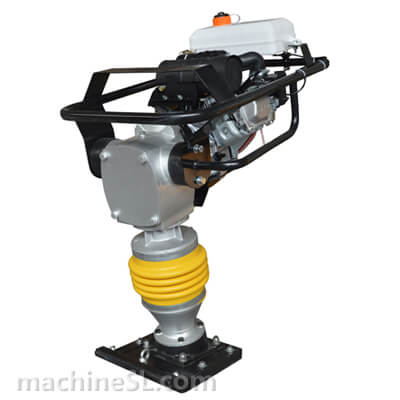
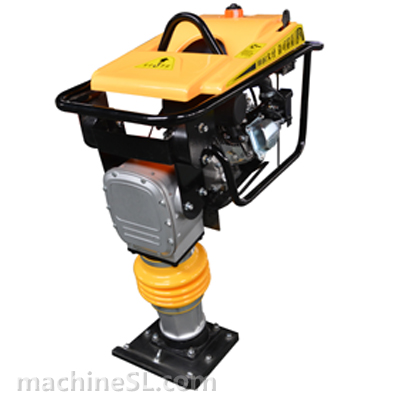
Cohesive soils include clayey silt, sandy clay, silty clay, clay and organic clay. Cohesive soils require high amplitude, high impact forces to squeeze and mold the material together, therefore are effectively compacted by the use of impact such as rammers or tamping rollers.
Cohesion less soil are the relatively clean sands and gravels that remain pervious even when well compacted. Cohensionless soil are those soil particles that is hard to stick together. Cohesion less soils pass through a #200 sieve, which has an opening size of 0.075 mm. Soil cohesion is closely related to soil consistency.
This type of soil can be coarse which contains stones, gravel or fine like sand or silt. In cases of cohensionless soil, the best way to effectively compact is by vibration. Excessive compaction can even lead to separating of soil particles rather than letting them stick together to remove the void content which is not good backfill.
Why Backfill Soil Compaction
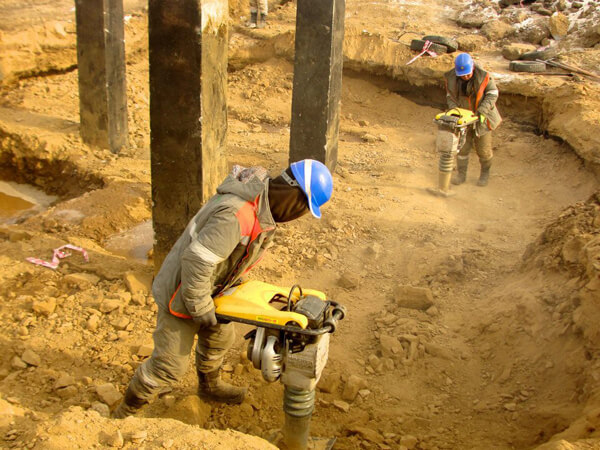

Backfilling is one of the essential task in the construction industry. This is the process of putting in soil, whether reusing or replacing, after the construction of structural member took place. The material used during the backfilling should comply to design requirements which means it can withstand the load transferred, maintaining the stability of the structure and does not impose significant settlement over time.
Factors you need to consider during backfilling are choosing the right soil and the compaction of soil. Ideally, backfill should be of material should be of small void material.
How to Compact Backfill
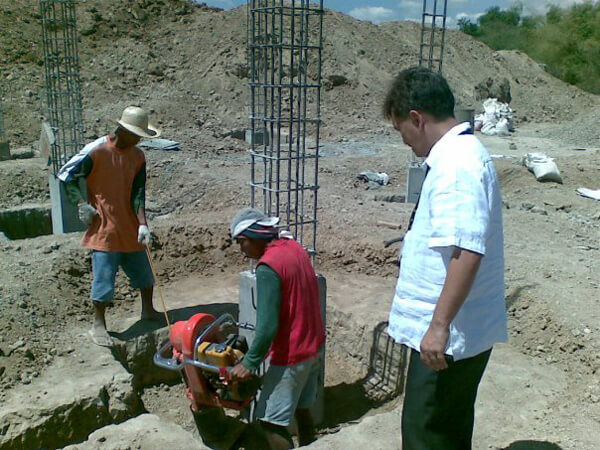

Soil compactor works in different ways like pressure, weight, impact, vibration and kneading. Some of the soil compactor can work one-way but because of the advancement of the technology, soil compactor equipment can work in many ways to be able to use it in different compaction job. Choosing which soil compactor greatly depends on many factors but most especially, the soil type.
For cohesive soil (fine-grained) type like clay, silt, sandy clay or silty clay, the compaction equipment best used are rammers, static sheepsfoot roller or pad foot/ tamping rollers.
For non-cohesive soil (coarse-grained) type like gravel or sand, the compaction equipment best used are smooth wheeled roller, rubber tired rollers or vibrating plate compactors.
There are other tools you can use to compact such as a lawn roller, hand tamper of sledge hammer. You must achieve a consistent amount of pressure and speed of rolling if you are using a roller. You must tamper/roll efficiently so that you will be able to distribute the required compaction on your entire area. If you are working with a great depth, you can do layering so you can make sure that every area are well compacted.
How to Calculate Backfill With Compaction Percentage

Backfills are usually compacted up to 25% of the fill volume. And the other hand, excavated materials are expected to expand up to 25% in volume when loaded for transport. To get the fill volume, you must multiply the actual volume to be filled by 1.25.
How to Backfill and Compact Driveway

To calculate the amount of backfill for the driveway first know your measurements of your driveway. Measure and record the length. After doing so, measure and record the width and the depth from different points in equally space interval until the end.
After measuring, calculate the average width and depth from the measurements taken. After having your length and average width and depth, calculate the volume of your driveway. Now to ensure that the volume of fill are enough, multiply with 1.25 in consideration of the contraction during the compaction.
Convert measurements if necessary according to how it is purchased.
For soil with high cohesion like clay, silts and clayey silts are harder to compact as they have higher resistance of their particles. Yet, granular soil, like sand, gravel and other coarse soils are easier to compact as they have higher density.
Moisture content plays a great role to execute compacting any kind of soil. Soil moisture should be the right amount before compaction. To ensure that you have achieved the required water content, you must use the hand test. Take a part of the soil and try molding it, if it breaks and crumbles, it is still dry and you need to add more water.
If the soil holds together, then you can now compact your entire area. And if you made it sticky, you need to dry it for a couple of time because it is too wet.
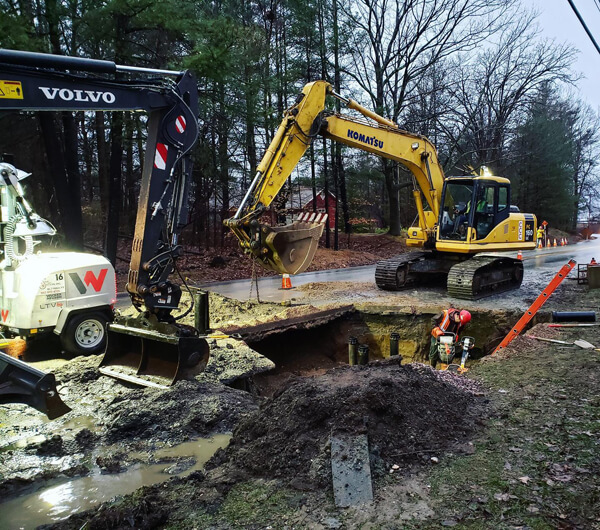
How to Compact Foundation Backfill

Initially, foundation should be cured as required before proceeding with the backfill process. The ground which will be filling with the soil material should be free from foreign material like loose stones, dirts and even ponding of water. Make sure that the surface is clean and corrective measure should be done.
Once the suitable backfill material is selected and passed the necessary testing, begin pouring the backfill material at the corners and make sure that the backfill material is evenly distributed along the sides in consecutive layers of 15 to 20 cm of each layer. Each layer should be compacted and watered. Repeat the procedure until the entire area is completely filled with backfill material.
Lastly, further compact the material and water them as necessary.
Prepare your backfill foundation, considering the sizes of the gravel making sure than once compacted, it will not overlap to your finish floor line. Start adding gravels few inches, wetting it will help, then start to compact the first layer of the gravel.
Check the firmness of the first layer, once it is stable enough, start adding more layer of gravels and start compacting.Check the levelness of the gravel bed and do until you get the desired thickness and level. Once done, sweep off the excess.
How to Compact Sand Backfill

Cohesion less soils are those which does not possess cohesion value. Cohesion value is either 0 or very less. These soils developer strength mainly through internal friction between particles. Sand is an example of cohesion less soils. These soils have shear strength dependent on angle of internal friction which depend on either the sand is loose, or dense.
For non-cohesive soil (coarse-grained) type like gravel or sand, the compaction equipment best used are smooth wheeled roller, rubber tired rollers or vibrating plate compactors.
Compaction after backfilling is an essential process after backfilling. Backfilling the structural members is not the last step but just the beginning to ensure the stability of the structure. Following the proper methodology to effectively compact the backfill material will not only save you time but also cost.
One important tip is always to consider the moisture content. Moisture content plays a big role in the compaction of loose backfill soil material. Adding water makes it easier to bind the soil particles as moisture penetrates the voids. Water content serves as a lubricant of the soil particles during the compaction. Compacting a over-saturated soil is an impossible job because water is incompressible.
Water content being the greater proportion in a soil mixture means it exceeds the liquid limit. And once this happens, its impossible to compress the soil any further.



























Leave A Comment